Bill Gates once said, “Automation applied to an efficient operation will magnify the efficiency.” Today, over 80% of business leaders agree—according to Gartner, automation is critical to maintaining competitiveness and profitability.
Business process automation speeds up repetitive tasks and approvals, reducing manual work and improving accuracy. With various types of business process automation available today, it’s important to understand which approach fits your organization best.
Read on to explore the types of business process automation, their benefits, and how FlowForma’s no-code tool can help you get your processes running like clockwork.
What is Business Process Automation (BPA)?
Business process automation (BPA) is an approach that uses software and technology to handle routine business tasks, making operations a cakewalk and enabling the business to run without interruptions.
These tasks include purchase orders, onboarding, and customer service, among several others.
Initially, BPA started small and focused on automating repetitive back-end tasks, but now plays a key role in digital transformation by applying AI and machine learning to automate both back-end and front-end processes.
This helps organizations optimize workflows across various departments, including supply chain, HR, finance, and customer service, among others. Increased productivity, scalability, and higher operational impact are a few benefits of business process automation.
The 5 Types of Business Process Automation
.png?width=650&height=488&name=Blue%20Gray%20Minimalist%20Circle%20Teamwork%20Infographic%20Presentation%20Graphs%20(3).png)
5 types of business process automation
All five types of business process automation serve a distinct purpose and provide unique benefits. Here’s a quick comparison of the types of business process automation:
|
Automation Type
|
Scope
|
Complexity
|
Technology Used
|
Best For
|
|
Task Automation
|
Single, repetitive tasks
|
Low
|
Scripts, no-code tools
|
Admin, HR, Finance
|
|
Workflow Automation
|
Multi-step processes
|
Low
|
No-code platforms, workflow tools
|
HR, Operations, Healthcare,
Construction, Banking, Insurance
|
|
RPA
|
High
volume tasks
|
Medium
|
Software bots
|
Manufacturing, Industrial-heavy industries
|
|
Hyper-automation
|
End-to-end processes
|
High
|
RPA + AI + ML + low code/no code platforms
|
Large global corporations with complex enterprise needs
|
|
Intelligent Automation
|
Cognitive, adaptive tasks
|
High
|
AI (ML, NLP, CV) + RPA
|
Data-heavy industries
|
Business process automation covers a range of solutions, from simple task automation to advanced intelligent automation. Each type helps organizations automate business processes by involving the right people, information, and steps.
While priorities differ across organizations, certain types of automation consistently improve productivity and reduce errors. Planning and modeling your processes is key to cutting out inefficiencies.
Now, we’ll explain the five types of business process automation in detail:
1. Task Automation
Task automation is the most fundamental type of business process automation. It focuses on automating simple, repetitive tasks that consume time but require little to no decision-making.
What is task automation?
Often, the first step in process optimization, task automation uses tools like scripts, macros, or no-code platforms to handle repetitive, rule-based work.
Common examples include data entry, report generation, and automated email alerts. These simple automations reduce manual errors, speed up execution, and let teams focus on higher-value tasks.
A good example is Coinford. The company used FlowForma, a no-code tool, to automate more than 10 quality assurance tasks. This enabled their teams to save 20% of time daily and 50% of admin time.
 A case study summary of how FlowForma helped Coinford LTD improve operational efficiency.
A case study summary of how FlowForma helped Coinford LTD improve operational efficiency.
Specifically, for ground bearing slab inspections, Coinford’s engineers and site managers received real-time alerts and completed digital checklists directly on-site. Reports were then automatically created and sent for client approval, simplifying the approval process and improving compliance.

Customer Feedback
Benefits of task automation
- Faster task completion: Automating routine tasks speeds up daily work, in turn avoiding delays
- Consistent accuracy: Automation follows precise rules, reducing errors that occurred in manual tasks
- Lower operational costs: Resources can be allocated for higher-value activities instead of routine tasks
- Boosted employee morale: Frees staff from mundane tasks so they focus on strategic, engaging work
- Rapid results: Easy to implement and delivers quick improvements that encourage wider automation adoption
Use cases of task automation
Task automation enables teams across a wide range of sectors, such as:
- Finance: Automating invoice processing, expense approvals, and payment reconciliations
- Human Resources: Automating employee data updates, benefits enrolment, and routine communications
- Customer Service: Sending automated responses to common inquiries or routing requests to the right teams
- Operations: Generating routine reports, updating inventory records, or scheduling maintenance tasks
Steps to implement task automation
-
Identify repetitive, rule-based tasks to automate
-
Choose user-friendly, no-code tools like FlowForma
-
Define simple, clear automation steps and rules
-
Test on a small scale before full rollout
-
Deploy, monitor performance, and collect feedback
-
Continuously refine and expand the automation
2. Workflow Automation
While task automation handles individual repetitive tasks, workflow automation manages entire sequences that make up a business process. It guarantees work moves smoothly from one step to the next by coordinating people, systems, and data for consistent and effective results.
What is workflow automation?
Workflow automation uses technology to control task flow within a process, linking tasks in order and managing approvals, notifications, and handoffs automatically. This reduces delays and errors and improves productivity.
For example, in employee onboarding, workflow automation can automatically route documents for approval, set up IT accounts, and schedule training, coordinated through a single process that tracks progress and keeps all stakeholders informed. The following case study further demonstrates this example.
Case Study: How Beaumont Hospital transformed patient onboarding and HR with FlowForma’s workflow automation
Beaumont Hospital used FlowForma to digitize patient onboarding and HR processes across 14 IT systems. Clinicians could capture data digitally at the bedside, instantly sharing it with back-office teams. This integration improved transparency, sped up workflows, and improved patient care by providing accurate, real-time data flow.

FlowForma’s customer feedback
How Beaumont Hospital transformed patient onboarding and HR with FlowForma’s workflow automation
Catch the full case study of workflow automation here.
Benefits of workflow automation
- Improved coordination: Automates handoffs and approvals, reducing delays and miscommunication
- Transparency: Provides real-time tracking and reporting on process status
- Consistency: Makes sure processes are followed exactly as designed, reducing compliance risks
- Increased productivity: Frees employees from manual follow-ups and status checks
- Scalability: Easily adapts to growing or changing business needs with customizable workflows
Tools such as FlowForma come with advanced features that further improve automation. These include:
- AI-powered Copilot: Quickly create and edit workflows using FlowForma’s AI Copilot that enables rapid process design without coding.
Watch this demo to learn how quickly Copilot can set up a commercial insurance renewal process:
A demo of a commercial insurance renewal process using FlowForma’s Copilot
- Governance and control: Improve oversight by involving all decision-makers and allowing IT to govern automation in a secure, controlled environment
- Collaboration: Improve cross-department teamwork with automated communications
- Quality and compliance: Standardize processes, increase visibility, and boost accountability and compliance across your workforce. In the demonstration below, you'll see how ISO compliance processes can be automated with an AI-powered Copilot.
FlowForma showcase of ISO automation
- Insights and reporting: Build dashboards in minutes to monitor process performance and business data from within the platform
- Integrations: Connect seamlessly with thousands of other systems, ensuring smooth data flow at every step
- Mobile access: Manage approvals, forms, and workflows anytime, anywhere via iOS and Android apps
- Document generation: Automate professional document creation at scale with a single click
Watch this video to learn more about FlowForma’s workflow automation features.
Learn more about FlowForma’s workflow automation features
Use cases of workflow automation
Workflow automation helps key business functions across sectors such as:
- Human Resources: Automating recruitment, onboarding, and performance reviews
- Finance: Streamlining purchase approvals, expense claims, and invoice processing
- Customer Service: Routing inquiries, managing service requests, and tracking resolutions
- Operations: Coordinating maintenance requests, quality checks, and compliance audits
- Healthcare: Managing patient scheduling, medical record processing, and treatment coordination
Steps to implement workflow automation
1. Document each step, decision point, and stakeholder involved in the workflow. Select a no-code tool like FlowForma that fits your technical environment and user needs

Mapping a process helps you find problems and make it simpler
2. Build the sequence of tasks, rules, and notifications
3. Connect relevant applications and data sources to automate data exchange
4. Run pilot tests to identify and fix issues before full deployment
5. Launch the workflow and track performance, making improvements as needed
6. Ensure all employees understand their roles and how to interact with the automated process
3. Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
The next type in the list is robotic process automation (RPA). While workflow automation manages the flow of tasks between people and systems, RPA mimics human actions within digital environments to execute high-volume transactions quickly and accurately.
What is robotic process automation?
This approach uses software “bots” to perform repetitive, rule-based tasks across multiple systems.
These software robots interact with applications just like a human would - logging in, copying and pasting data, filling forms, extracting information, and more. They work tirelessly around the clock, handling routine tasks that would otherwise require manual effort.
A classic example is Wells Fargo, an American multinational financial services company, which has broadly expanded its use of robotic process automation across key operations.
The bank now deploys advanced RPA solutions for real-time fraud detection, where bots continuously analyze transaction patterns to flag suspicious activities. RPA is also used for account closure processes, where automation makes swift and accurate handling possible. This led to improvements in operational efficiency, security, and customer experience.


US-based Wells Fargo uses RPA to increase operational efficiency
Benefits of robotic process automation
- Increased speed: Bots work 24/7, completing tasks faster than humans
- Cost-effective: Automates labor-intensive tasks, reducing operational costs
- Reliable & accurate: Reduces human errors in repetitive data handling
- Scalable & productive: Easily scales by adding more bots to handle increased workloads
- Non-intrusive: Operates without disrupting existing legacy systems, easing the workload on IT teams
Use cases of robotic process automation
- Banking and Finance: Automating loan processing, transaction reconciliation, and compliance reporting
- Insurance: Simple claims processing, policy administration, and fraud detection
- Manufacturing: Inventory updates, order processing, and supplier communications
- Customer Service: Data validation, account updates, and ticket routing
Steps to implement robotic process automation
-
Look for high-volume, repetitive, rule-based tasks that involve multiple systems
-
Choose RPA software that fits your IT environment and business needs
-
Configure bots to perform the identified tasks, often with minimal coding
-
Run pilots to ensure bots perform accurately and handle exceptions
-
Roll out bots across departments, monitoring performance and impact
-
Continuously monitor bots and update them as processes or systems change
4. Hyper-automation
Hyper- automation combines multiple technologies such as robotic process automation (RPA), artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and low-code/no-code tools to automate complex, end-to-end business processes. It integrates these tools to rapidly identify, automate, and optimize workflows, improving speed, accuracy, and efficiency across the organization.
What is hyper-automation?
Hyper- automation manages repetitive tasks as well as complex decision-making and process improvements. It involves discovering which processes can be automated, designing workflows, deploying bots, applying AI for cognitive tasks, and using analytics to monitor and refine operations.
Unlike RPA or workflow automation alone, hyper- automation automates entire business functions across departments, breaking down silos and enabling smooth collaboration.
For instance, Siemens, an engineering tech company, used hyper- automation to improve manufacturing processes, enable predictive maintenance, and implement real-time quality control, resulting in increased operational efficiency and reduced downtime.
Benefits of hyper-automation

Benefits of hyper-automation
Use cases of hyper-automation
Hyper- automation is used in various sectors such as:
- Supply chain management: Automating procurement, inventory management, logistics, and supplier communications
- Customer experience: Integrating chatbots, CRM automation, and service workflows for improved customer experiences
- Finance and accounting: Automating order-to-cash, record-to-report, and compliance processes with AI-powered insights
- Healthcare: Coordinating patient care workflows, claims processing, and regulatory reporting
Steps to implement hyper-automation
-
Use process mining and analytics to find automation opportunities throughout the organization
-
Choose processes that are impactful and feasible to automate
-
Build the automation setup by combining RPA, AI, ML, and workflow tools based on your needs
-
Design and deploy automation components with smooth integration into existing systems
-
Continuously monitor performance using AI-driven analytics to improve processes
-
Expand automation to more processes and departments while maintaining proper governance
5. Intelligent Automation
Intelligent automation is a mix of traditional automation methods like RPA and workflow automation with advanced AI technologies such as machine learning (ML), natural language processing (NLP), and computer vision. This mix helps automation systems process complex, unstructured data and make decisions that require human judgment.
What is intelligent automation?
Unlike rule-based automation, intelligent automation uses AI to interpret information, learn from data, and adapt over time. It can analyze documents, understand language, recognize images, and predict outcomes, enabling businesses to automate tasks that involve variability, ambiguity, or require cognitive abilities.
For example, instead of just transferring data between systems, intelligent automation can extract information from invoices, categorize documents, or respond to customer inquiries using natural language understanding.
Tech Mahindra supported a major oil producer in Oman by implementing intelligent automation for data collection, reconciliation, and reporting. By combining AI with automation, they reduced human errors, doubled processing speed, and saved about $1.6 million. The system adapted to changing data patterns, providing ongoing improvements.
Benefits of intelligent automation
.png?width=640&height=480&name=Blue%20Gray%20Minimalist%20Circle%20Teamwork%20Infographic%20Presentation%20Graphs%20(4).png)
Benefits of intelligent automation
- Context-aware accuracy: AI reduces errors by understanding context and nuances in data
- Complex task automation: Automates complex semi-automated or manual tasks
- Adaptive learning: Learns and adapts to new scenarios, reducing the need for constant reprogramming
- Personalized speed: Enables faster, more personalized responses and services
- Compliance monitoring: Detects anomalies and ensures adherence to the government or organization’s regulations
Use cases of intelligent automation
Sectors that benefit from intelligent automation include:
- Finance: Automating invoice processing by extracting data from diverse formats and validating entries
- Healthcare: Digitizing patient records, coding medical documents, and managing claims
- Customer Service: AI-powered chatbots that understand and respond to customer inquiries
- Insurance: Fraud detection through pattern recognition and claim validation
- Manufacturing: Predictive maintenance by analyzing sensor data and scheduling repairs proactively
Steps to implement intelligent automation
-
Identify complex tasks
-
Choose appropriate AI tools like NLP, ML, or computer vision based on the task
-
Combine AI models with RPA and workflow automation for end-to-end solutions
-
Use historical data to train and validate AI components
-
Test intelligent automation in controlled environments, gather feedback, and improve accuracy.
-
Roll out across the organization with ongoing monitoring and model updates
Simplify Business Process Automation with FlowForma
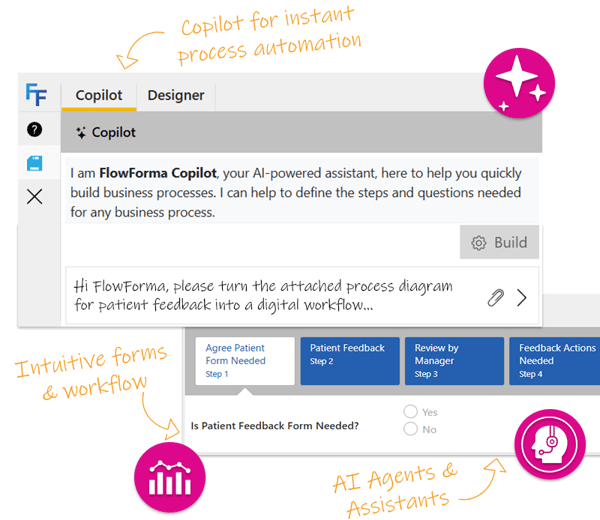 FlowForma, an AI-driven no-code workflow automation tool
FlowForma, an AI-driven no-code workflow automation tool
When it comes to AI-driven, no-code business process automation, FlowForma is a cut above the rest due to the following reasons:
- Fast deployment: Can automate processes up to 5x faster than traditional tools.
- User-friendly: Has an intuitive interface that lets non-technical users build workflows with ease
- Smooth integration: Works with thousands of existing systems, including Microsoft 365 and Google
- Governance and compliance: Backed with strong IT controls to maintain security and compliance
- Quicker processing time: Built to work with Microsoft 365, FlowForma helps reduce process times and cuts manual errors significantly.
Ready to get started? Book a demo to explore the potential for your business.

.png)

.png?width=650&height=488&name=Blue%20Gray%20Minimalist%20Circle%20Teamwork%20Infographic%20Presentation%20Graphs%20(3).png)





.png?width=640&height=480&name=Blue%20Gray%20Minimalist%20Circle%20Teamwork%20Infographic%20Presentation%20Graphs%20(4).png)




